12-07-2025, 02:28 AM
Please correct this drap and drop as some of the answers that show as "correct" are wrong.
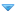
[*]✅ Correct vs Incorrect:
[*]This is what is actually correct:
[*]Monitor mode →
monitor for rogue APs, does not handle data at all
(Used for detecting rogue access points and IDS/IPS scanning.)
[*]Bridge mode →
preferred for connecting access points in a mesh environment
(AP acts as a bridge between two networks, common in mesh setups.)
[*]FlexConnect mode →
allows the access point to communicate with the WLC over a WAN link
(Ideal for remote sites where APs connect to a central WLC over WAN.)
[*]Local mode →
transmits normally on one channel and monitors other channels for noise and interference
(Default mode for APs; serves clients and performs RRM scanning.)
[*]Rogue detector mode →
receive only mode which acts as a dedicated sensor for RFID and IDS
(Used for detecting rogue devices; does not transmit.)
[*]Sniffer mode →
allows for packet captures of wireless traffic
(Captures 802.11 frames for analysis in Wireshark or similar tools.)
[*]✅ Correct vs Incorrect:
- Sniffer mode: allows for packet captures of wireless traffic.
✔ Correct – Sniffer mode is used for capturing 802.11 frames for analysis.
- FlexConnect mode: allows the access point to communicate with the WLC over a WAN link.
✔ Correct – FlexConnect is designed for remote sites where APs connect to WLC over WAN.
- Monitor mode: receive only mode which acts as a dedicated sensor for RFID and IDS.
❌ Incorrect – Monitor mode is for detecting rogue APs and IDS scanning, not RFID. It does not serve clients.
- Bridge mode: preferred for connecting access points in a mesh environment.
✔ Correct – Bridge mode is used for mesh APs or point-to-point bridging.
- Local mode: transmits normally on one channel and monitors other channels for noise and interference.
✔ Correct – Local mode serves clients and performs RRM scanning.
- Rogue detector mode: monitor for rogue APs, does not handle data at all.
❌ Incorrect – Rogue detector mode listens for MAC addresses from wired networks to detect rogue APs, not wireless monitoring.
[*]This is what is actually correct:
[*]Monitor mode →
monitor for rogue APs, does not handle data at all
(Used for detecting rogue access points and IDS/IPS scanning.)
[*]Bridge mode →
preferred for connecting access points in a mesh environment
(AP acts as a bridge between two networks, common in mesh setups.)
[*]FlexConnect mode →
allows the access point to communicate with the WLC over a WAN link
(Ideal for remote sites where APs connect to a central WLC over WAN.)
[*]Local mode →
transmits normally on one channel and monitors other channels for noise and interference
(Default mode for APs; serves clients and performs RRM scanning.)
[*]Rogue detector mode →
receive only mode which acts as a dedicated sensor for RFID and IDS
(Used for detecting rogue devices; does not transmit.)
[*]Sniffer mode →
allows for packet captures of wireless traffic
(Captures 802.11 frames for analysis in Wireshark or similar tools.)